- Azure Remote Desktop Services Cost
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Services
- Azure Remote Desktop Services Pricing
- Azure Remote Desktop Services Architecture
Remote Desktop to Azure AD Joined Computer Unfortunately, at this time it isn’t quite as easy as “open up a new RDP connection, type in the computer, type my email, and connect”. If it were, this post wouldn’t be here. Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is the platform of choice to cost-effectively host Windows desktops and applications. This offering is designed to help you quickly create a RDS on IaaS deployment for testing and proof-of-concept purposes. Access desktops powered by Windows Server Remote Desktop Services desktops and apps at no additional cost if you are an eligible Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Client Access License (CAL) customer. You need an Azure account to quickly. How to set up the DNS name for a new Azure Resource Manager VM to RDP via port 3389 to the Remote Desktop Access.
-->Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is the platform of choice to cost-effectively host Windows desktops and applications. You can use an Azure Marketplace offering or a quickstart template to quickly create an RDS on Azure IaaS deployment. Azure marketplace creates a test domain for you, making it a simple and easy mechanism for testing and proof-of-concepts. The quickstart templates, on the other hand, allow you to use an existing domain, making them a great tool to build out a production environment. Once set up, you can connect to the published desktops and applications from various platforms and devices, using the Microsoft Remote Desktop apps for Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android.
Basic RDS through the Azure Marketplace
Creating your deployment through the Azure Marketplace is the quickest way to get up and running. When everything is completed, your environment will look like the basic RDS architecture. The offering creates all the RDS components that you need - all you need to do is supply some information.

You'll need to supply the following information when you deploy the Marketplace offering:
- Administrator user name and password. This is a new user that will manage the deployment.
- DNS name and AD domain name. These are NEW resources that are created. Make sure the names are meaningful.
- VM size. You get to choose the size of VMs to use for the RDSH endpoints. You can also manually change the sizes after the initial deployment to help you optimize the VMs for your workloads and for cost.
Use these steps to create your small-footprint RDS deployment from the Azure Marketplace:
- Launch the Azure Marketplace RDS deployment:
- Sign into the Azure portal.
- Click New to add your deployment.
- Type 'RDS' in the search field and press Enter.
- Click Remote Desktop Services (RDS) - Basic - Dev/Test, and then click Create.
- Follow the steps in the portal to create and deploy RDS. You'll add key configuration details, like the information listed above.
- Connect to your deployment. When the deployment finishes, check the outputs section for final steps to complete and connect to your deployment.
Download and run this PowerShell script on your test device to install any certificates needed to connect to the RDS deployment.
This step is only necessary during the testing phase. When you deploy RDS in Azure in production, make sure to follow best practices like purchasing and using a publicly trusted SSL certificate on your web servers.
When prompted, sign into your Azure account. Select the Azure subscription, resource group, and public IP address created for this new deployment.
When the script is finished, the RD Web page launches in your default browser. You can double-check the RD Web page by comparing the URL for the page to the DNS address you provided during deployment.
Sign in with the admin credentials you created during deployment to see the default desktop published for you. You can also send users the RD Web site to test their desktops and applications.
Tip
Forget the domain name or admin user? You can go back to the new Resource Group in the portal, click Deployments, and then view the parameters you entered.
Now that you have an RDS deployment, you can add and manage users.

Customized RDS using Quickstart templates
You can use Azure Resource Manager templates to deploy RDS in Azure. This is especially useful if you want a basic RDS deployment but have existing components (like AD) that you want to use. Unlike the Marketplace offering, you can make further customizations, such as using an existing AD on a virtual network, using a custom OS image for the RDSH VMs, and layering on high availability for RDS components. After adding on high availability to each component, your environment will look like the highly availabile RDS architecture.
Use these steps to create your small-footprint RDS deployment with an Azure RDS template:
- Pick your Azure Quickstart template:
- Go to the RDS Azure Quickstart Templates site.
- Choose the template that matches what you are trying to do. Make sure you meet any prerequisites for that specific template. (For example, if you are want to use a custom image for your VMs, make sure you have already uploaded that image to an Azure storage account.)
- Click Deploy to Azure.
- You'll need to provide some details (like admin user name, AD domain name) in the Azure portal. This varies based on the template you choose.
- Click Purchase.
- Connect to your deployment.
Download and run this PowerShell script on your test device to install any certificates needed to connect to the RDS deployment.
This step is only necessary during the testing phase. When you deploy RDS in Azure in production, make sure to follow best practices like purchasing and using a publicly trusted SSL certificate on your web servers.
When prompted, sign into your Azure account. Select the Azure subscription, resource group, and public IP address created for this new deployment.
When the script is finished, the RD Web page launches in your default browser. You can double-check the RD Web page by comparing the URL for the page to the DNS address you provided during deployment.
Sign in with the admin credentials you created during deployment to see the default desktop published for you. You can also send users the RD Web site to test their desktops and applications.
Tip
Forget the domain name or admin user? You can go back to the new Resource Group in the portal, click Deployments, and then view the parameters you entered.
Now that you have an RDS deployment, you can add and manage users.
-->Azure Remote Desktop Services Cost
Important
Azure Cloud Services (extended support) is a new Azure Resource Manager based deployment model for the Azure Cloud Services product. With this change, Azure Cloud Services running on the Azure Service Manager based deployment model have been renamed as Cloud Services (classic) and all new deployments should use Cloud Services (extended support).
Remote Desktop enables you to access the desktop of a role running in Azure. You can use a Remote Desktop connection to troubleshoot and diagnose problems with your application while it is running.
You can enable a Remote Desktop connection in your role during development by including the Remote Desktop modules in your service definition or you can choose to enable Remote Desktop through the Remote Desktop Extension. The preferred approach is to use the Remote Desktop extension as you can enable Remote Desktop even after the application is deployed without having to redeploy your application.
Configure Remote Desktop from the Azure portal
The Azure portal uses the Remote Desktop Extension approach so you can enable Remote Desktop even after the application is deployed. The Remote Desktop settings for your cloud service allows you to enable Remote Desktop, change the local Administrator account used to connect to the virtual machines, the certificate used in authentication and set the expiration date.
Click Cloud Services, select the name of the cloud service, and then select Remote Desktop.
Choose whether you want to enable Remote Desktop for an individual role or for all roles, then change the value of the switcher to Enabled.
Fill in the required fields for user name, password, expiry, and certificate.
Warning
All role instances will be restarted when you first enable Remote Desktop and select OK (checkmark). To prevent a reboot, the certificate used to encrypt the password must be installed on the role. To prevent a restart, upload a certificate for the cloud service and then return to this dialog.
In Roles, select the role you want to update or select All for all roles.
When you finish your configuration updates, select Save. It will take a few moments before your role instances are ready to receive connections.
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services
Remote into role instances
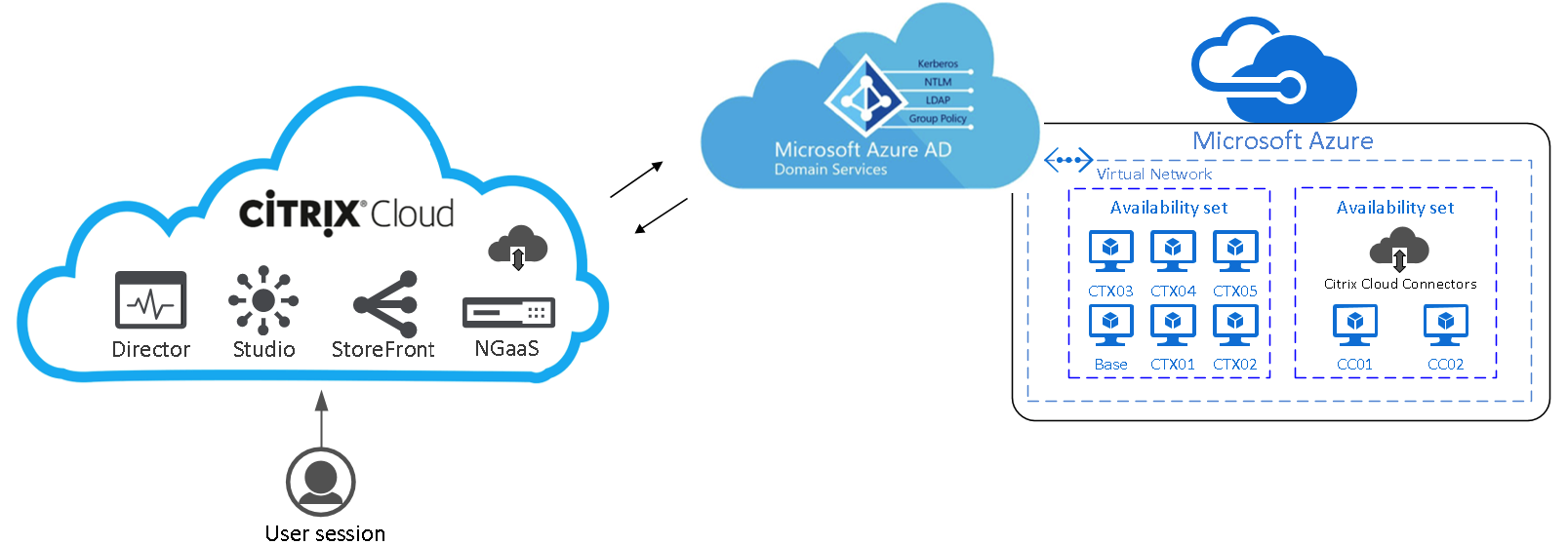
Azure Remote Desktop Services Pricing
Once Remote Desktop is enabled on the roles, you can initiate a connection directly from the Azure portal:
Azure Remote Desktop Services Architecture
Click Instances to open the Instances settings.
Select a role instance that has Remote Desktop configured.
Click Connect to download an RDP file for the role instance.
Click Open and then Connect to start the Remote Desktop connection.
Note
If your cloud service is sitting behind an NSG, you may need to create rules that allow traffic on ports 3389 and 20000. Remote Desktop uses port 3389. Cloud Service instances are load balanced, so you can't directly control which instance to connect to. The RemoteForwarder and RemoteAccess agents manage RDP traffic and allow the client to send an RDP cookie and specify an individual instance to connect to. The RemoteForwarder and RemoteAccess agents require that port 20000* is open, which may be blocked if you have an NSG.
Additional resources
